

It was originally developed to be used for solving complex maths problem around transmission lines and matching circuits which has now been replaced by computer software. The Smith chart is a ‘backof-the-envelope’ tool that designers use to sketch out designs. The Smith Chart, named after its Inventor Phillip Smith, developed in the 1940s, is essentially a polar plot of the complex reflection coefficient for arbitrary impedance. The measurement procedure is as follows: 1) Connect the section of cable to be tested to the analyzer and leave the other end unterminated. It’s a graphic of the reflection coefficient in polar coordinates. The chart is part of current CAD tools and modern measurement equipments.
Using a smith chart manual#
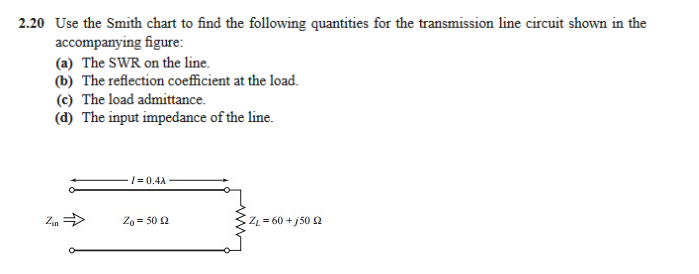
of the User’s Manual as a method to determine the length of a cable and cancel the effect of it using the Transmission Line Subtract feature. Smith Chart Parametric Equations r L circles r L circles are contained inside the unit circle Each node on the chart will tell us about the load characteristics and coef. The complex impedance (or admittance )is normalized using a reference, which usually is the characteristic impedance Z 0. The Smith chart presents a large amount of information in a confined space and interpretation, such as applying appropriate signs, is required to extract values. The Smith Chart unwrap method is described in section 4.1. This section first presents the impedance Smith chart and then the admittance Smith chart before introducing a combined Smith chart which is the form needed in design. Interactive Smith chart Impedance matching The interactive Smith chart enables users to navigate their way around a Smith chart, using simple discrete element impedance matching. Smith Charts can be used to increase understanding of transmission lines and how they behave from an impedance viewpoint. Once around the circle is a line length of l/2. The impedance is represented by a normalized impedance z. It also allows the calculation of the admittance Y 1/Z of an impedance. Smith Chart: The Smith Chart is a fantastic tool for visualizing the impedance of a transmission line and antenna system as a function of frequency. The Smith Chart The Smith Chart allows easy calculation of the transformation of a complex load impedance through an arbitrary length of transmission line. Only a few have survived in electrical engineering usage, with Smith charts being overwhelmingly the most important. SMITH CHART, SOLUTIONS OF PROBLEMS USING SMITH CHART. Design using Smith charts will be considered in other chapters but at this stage the reader should be totally conversant with the techniques described in this section. Once nomographs and graphical calculators were common engineering tools mainly because of limited computing resources. The Smith chart is the most powerful of tools used in RF and Microwave Design. The Smith chart was invented by Phillip Smith and presented in close to its current form in 1937, see. Plot the normalized impedance, determine the normalized admittance, determine the actual admittance, calculate VSWR, and the reflection coefficient. The chart has many numbers printed in quite small font and with signs dropped as there is not room. A 50ohm lossless transmission line is terminated in a complex load impedance of 40 + j70ohms. It takes effort to master but fundamentally it is quite simple combining a polar plot used for plotting \(S\) parameters directly, curves that enable normalized impedances and admittances to be plotted directly, and scales that enable electrical lengths in terms of wavelengths and degrees to be read off. The easiest way to verify that the calibration procedure has been done correctly is by utilizing a Smith chart menu on a network analyzer. Network analyzer measurements require the calibration procedure which utilizes a calibration kit, consisting of a short, open, and a 50 load attachment. Mastering the Smith chart is essential to entering the world of RF and microwave circuit design as all practitioners use this as if it is well understood by others. Smith Chart Basics: Network Analyzer Calibration. We will use the Smith Chart to calculate a tuner that matches a 25 ohm resistive load to a 50 ohm transmission line at 100 MHz.

Although the Smith chart is rather old, it is a common design tool in electromagnetics. Smith Chart plots the reflection coefficient () which is related to the impedance by: Á L Á O à L < F < 4 < E < 4 L 7 E F 8 Here Z0 is the characteristic impedance of the transmission line or just some reference impedance for the Smith Chart. As such, it allows calculations of all parameters related to transmission lines as well as impedances in open space, circuits, and the like. Example \(\PageIndex = −60.8\:\Omega\).The Smith chart is a powerful graphical tool used in the design of microwave circuits. The Smith chart is a chart of normalized impedances (or admittances) in the reflection coefficient plane.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
